Aquaponics: Symbiotic Cultivation of Fish and Vegetables
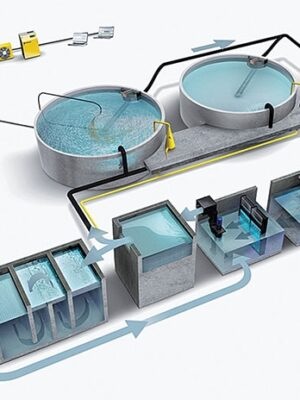
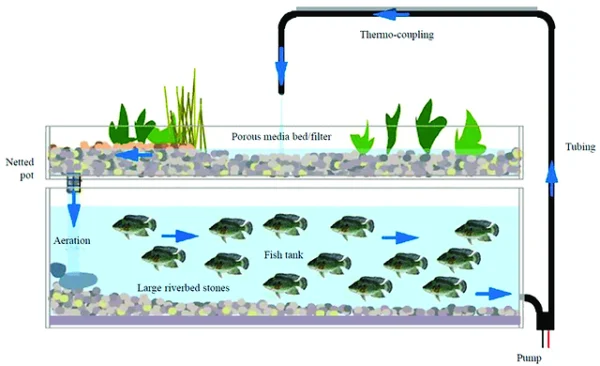
The integration of fish and vegetable co-culture technology, commonly referred to as Aquaponics, represents an innovative and sustainable approach to aquaculture and hydroponics. Aquaponics combines the cultivation of fish and plants in a symbiotic environment, where the waste produced by aquatic animals serves as nutrients for plants, and the plants, in turn, purify the water for the fish.
The integration of fish and vegetable co-culture technology, commonly referred to as Aquaponics, represents an innovative and sustainable approach to aquaculture and hydroponics. Aquaponics combines the cultivation of fish and plants in a symbiotic environment, where the waste produced by aquatic animals serves as nutrients for plants, and the plants, in turn, purify the water for the fish.
1. Closed-loop Ecosystem:
– Aquaponics creates a closed-loop system that mimics natural ecological processes. Fish waste provides an organic nutrient source for the plants, while the plants filter and clean the water, which is then recirculated back to the fish tanks.
2. Resource Efficiency:
– This system significantly reduces the need for external nutrient inputs and water usage, making it an exceptionally resource-efficient method for producing food. It is ideal for areas with limited water resources or where sustainable water use is a priority.
3. Organic Production:
– Aquaponics systems typically avoid the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, promoting organic cultivation methods. The absence of soil also minimizes the risks of soil-borne diseases and pests.
4. Scalability and Versatility:
– Aquaponics systems can be scaled from small, backyard setups to large commercial operations. They can be adapted to various environments, including urban areas, deserts, and regions with poor soil quality.
5. Research and Innovation:
– Ongoing research and development in aquaponics focus on optimizing system designs, enhancing the efficiency of nutrient cycling, selecting suitable plant and fish species, and automating system components for better productivity and ease of management.
6. Educational and Community Benefits:
– Aquaponics serves as an educational tool for teaching principles of biology, ecology, and sustainable agriculture. It also has the potential to bolster local food systems, improve food security, and support community-based agriculture initiatives.
7. Products and Services:
– Companies specializing in aquaponics offer a range of products and services, including system design and installation, training and consultancy, seedlings and juvenile fish, and support for system management and optimization.
Aquaponics stands out as a futuristic model of agriculture that aligns with goals of sustainability, efficiency, and the integration of technology into food production. Its role in aquaculture technology research and development is pivotal, offering pathways to address food production challenges while minimizing environmental impacts.